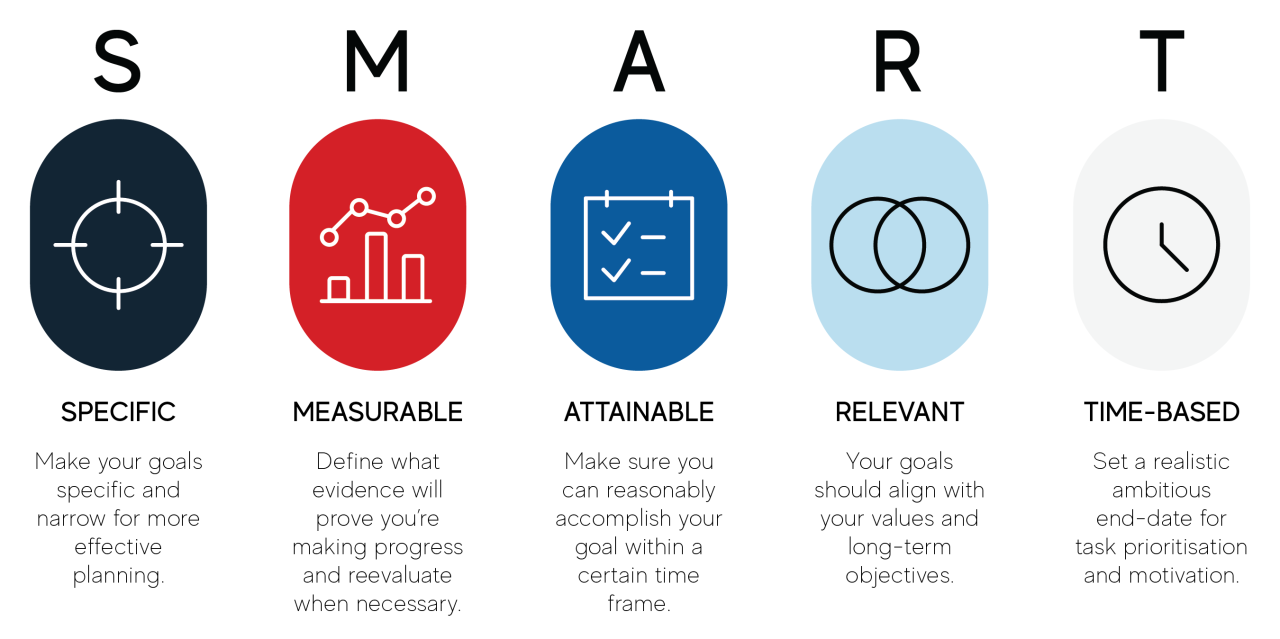
Smart gateway sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a technology that transforms how devices communicate and interact within our environments. This innovative system serves as a bridge between various devices and networks, enabling seamless connectivity and efficient management of resources.
By leveraging smart gateways, users can experience enhanced automation, improved data management, and increased interoperability across multiple platforms, making them a cornerstone in the evolution of smart homes, cities, and industries.
Overview of Smart Gateway Technology
Smart gateways serve as a crucial component in the realm of Internet of Things (IoT) technology, functioning as the central hub that connects various devices within a network. They facilitate communication between devices, cloud services, and applications, allowing for seamless integration and control. By acting as intermediaries, smart gateways enhance the functionality of connected devices, enabling them to work together more efficiently.
The primary functionality of smart gateways lies in their ability to process and manage data traffic. They perform essential tasks such as data aggregation, protocol translation, and device management. This not only optimizes network performance but also ensures security by safeguarding sensitive information. The advantages of implementing smart gateways span multiple applications, notably in smart homes, industrial automation, and urban infrastructure. The integration of smart gateways leads to enhanced device interoperability, reduced latency, and improved user experiences.
Advantages and Benefits of Smart Gateways
Smart gateways offer numerous benefits that significantly enhance the performance and efficiency of connected devices. Their advantages can be categorized into several key areas:
- Interoperability: Smart gateways enable different devices, often from various manufacturers, to communicate effectively, ensuring a cohesive ecosystem.
- Data Management: They manage the flow of data between devices and the cloud, allowing for real-time analytics and decision-making.
- Security: Smart gateways incorporate security protocols to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches, safeguarding user information.
- Scalability: By facilitating the addition of new devices without significant infrastructure changes, smart gateways support the growth of IoT networks.
- Energy Efficiency: They optimize energy consumption by managing device operations, contributing to cost savings and sustainability.
The implementation of smart gateways in smart homes exemplifies these advantages. In a typical smart home setup, the gateway acts as the central controller that connects devices such as smart thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras. With the smart gateway, users can remotely monitor and control their home environment through a single application, regardless of the device’s manufacturer. For example, a homeowner can adjust the thermostat, turn on lights, and receive alerts from security cameras, all through the gateway interface. This level of integration not only simplifies user experience but also promotes energy efficiency by enabling smart scheduling and automation of tasks.
“In smart homes, the ability of a gateway to integrate devices not only enhances convenience but also contributes to smarter energy management and security.”
Smart Gateway Protocols and Standards
Smart gateway technology serves as a pivotal component in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem, enabling seamless communication between various device types. Understanding the protocols and standards that govern these gateways is crucial for ensuring interoperability and efficiency across different platforms and applications.
Smart gateways utilize a variety of protocols to facilitate communication between IoT devices, cloud services, and users. These protocols ensure data is transmitted securely, efficiently, and accurately across diverse networks. The key protocols involved include MQTT, CoAP, HTTP/HTTPS, and AMQP, each serving distinct purposes and offering unique advantages.
Key Protocols Used in Smart Gateway Technology
The following protocols play significant roles in the functioning of smart gateways:
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): A lightweight messaging protocol ideal for low-bandwidth, high-latency networks. MQTT is widely used due to its simplicity and effectiveness in transmitting data from remote sensors to the gateway.
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol): Designed specifically for resource-constrained devices, CoAP enables efficient communication between devices and the web, supporting RESTful interaction, making it suitable for IoT applications.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Traditional web protocols that provide a robust method for data transmission over the internet. HTTPS ensures secure communication, making it essential for applications requiring data privacy.
- AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol): A messaging protocol that allows for message-oriented middleware, ensuring reliable communication between applications, particularly in enterprise environments.
The choice of protocol impacts the scalability and performance of smart gateways. Each protocol’s design reflects the specific requirements of various IoT applications, influencing factors like bandwidth, power consumption, and complexity.
Comparison of Communication Standards Utilized by Smart Gateways
The communication standards implemented by smart gateways vary in their capabilities, strengths, and intended applications. Here’s a comparative overview of some prevalent standards:
| Standard | Usage | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Zigbee | Short-range, low-power devices | Mesh networking, low power consumption, ideal for home automation |
| Z-Wave | Home automation | Low power, reliable, operates in the sub-1 GHz range, minimizing interference |
| Wi-Fi | High-bandwidth applications | High speed, widespread availability, suitable for data-heavy tasks |
| LoRaWAN | Long-range, low-power networks | Long-range communication, ideal for outdoor IoT applications |
These communication standards are essential to understand as they influence the design and deployment of smart gateways. Each standard has its unique advantages, making them suitable for different scenarios within the IoT landscape.
Interoperability Among Different Devices Through Smart Gateways
Interoperability is a critical aspect of smart gateways, allowing different IoT devices to communicate effectively regardless of the manufacturer or protocol they utilize. This is achieved through several mechanisms:
- Protocol Translation: Smart gateways often incorporate functionality that translates between various communication protocols, enabling devices using different standards to interact.
- Data Normalization: Gateways can standardize data formats, ensuring consistent data representation across diverse devices, thus simplifying processing and analysis.
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): By exposing APIs, smart gateways enable third-party applications to interface with a variety of devices, enhancing functionality and expanding the ecosystem.
- Edge Computing: Performing computations at the edge reduces latency and bandwidth usage, allowing devices to communicate efficiently without necessitating constant cloud interaction.
The focus on interoperability ensures that smart gateways remain versatile, supporting a broad range of devices and applications while promoting innovation and integration within the IoT landscape.
Applications of Smart Gateways in Various Industries
Smart gateways play a crucial role in various industries by facilitating communication between devices, enhancing data management, and improving operational efficiency. These technologies are pivotal in transforming traditional systems into smart environments, particularly in urban settings, transportation networks, healthcare facilities, and energy management systems. Their ability to aggregate, process, and transmit data makes them essential for the development of interconnected applications that drive innovation and improve service delivery.
Smart gateways serve as the backbone of smart city infrastructure, enabling seamless connectivity between various components such as traffic systems, public safety networks, and utility management. Their integration enhances real-time data collection and monitoring, which is vital for efficient city management.
Impact of Smart Gateways in Key Sectors
The influence of smart gateways extends across various sectors, significantly improving operational effectiveness and service delivery. The following table summarizes the impact of smart gateways in healthcare, transportation, and energy sectors:
| Sector | Impact |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Enhanced patient monitoring through real-time data transmission, which improves treatment outcomes and reduces hospital stays. |
| Transportation | Optimized traffic management and reduced congestion through real-time data analysis, improving travel efficiency and safety. |
| Energy | Improved energy management and reduced wastage through smart metering and real-time monitoring of energy consumption. |
The benefits of smart gateways are clear in the context of their application, with each sector experiencing significant advancements due to the adoption of these technologies.
Case Studies of Smart Gateways in Industrial Settings
Numerous industries have successfully implemented smart gateways to enhance their operations. Notable case studies illustrate these successful implementations:
1. Healthcare Sector: The deployment of smart gateways in hospitals has enabled continuous remote patient monitoring, facilitating timely interventions. For instance, a major healthcare provider in the United States integrated smart gateways with wearable health devices, allowing healthcare professionals to monitor patients’ vital signs in real-time, which led to a 30% reduction in emergency room visits.
2. Transportation Sector: A smart city initiative in Barcelona utilized smart gateways to connect traffic lights, vehicles, and public transport systems. This integration helped reduce traffic congestion by 25% and improved public transport efficiency by allowing real-time adjustments based on traffic flow data.
3. Energy Sector: In Germany, a leading energy company implemented smart gateways in a grid modernization project. The deployment allowed for real-time monitoring of energy consumption across urban areas, resulting in a more efficient distribution of resources and a decrease in energy costs by approximately 15% for consumers.
Each of these case studies highlights the transformative potential of smart gateways in enhancing operational efficiency and service delivery across various sectors, thereby paving the way for future advancements in technology and infrastructure.
Future Trends in Smart Gateway Development
The landscape of smart gateway technology is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in connectivity, security, and data management. As the backbone of IoT ecosystems, smart gateways play a pivotal role in bridging the gap between devices and cloud platforms. This section delves into the current trends shaping the evolution of smart gateways, alongside predictions for their future capabilities and the emerging technologies that will influence their development.
Current Trends in Smart Gateway Technology
Several trends are currently shaping the development of smart gateway technology. These trends are characterized by increased integration, enhanced security measures, and the push towards greater interoperability among devices.
One significant trend is the move towards edge computing, where data processing occurs closer to the data source rather than relying solely on centralized cloud systems. This shift reduces latency and bandwidth consumption, leading to faster response times. Additionally, as security concerns rise, smart gateways are increasingly incorporating advanced security protocols, such as end-to-end encryption, to safeguard data transmission between devices and networks.
Predictions for Future Capabilities of Smart Gateways
Looking ahead, smart gateways are expected to incorporate a variety of advanced functionalities that will enhance their performance and utility. The following capabilities are predicted to emerge in the coming years:
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: Future smart gateways will likely feature integrated AI algorithms that enable predictive analytics and automated decision-making, facilitating smarter device management and energy consumption optimization.
- Enhanced Interoperability: With the push towards universal standards, future gateways will support a wider range of protocols, allowing seamless communication between diverse devices across various ecosystems.
- Increased Automation: Automation capabilities will expand, allowing smart gateways to intelligently manage and configure connected devices based on real-time data and user behavior.
- Blockchain for Security: The integration of blockchain technology may provide enhanced security and transparency in data handling, ensuring that transactions between devices are immutable and verifiable.
Emerging Technologies Influencing Smart Gateways
Several emerging technologies are poised to influence the development of smart gateways significantly. These technologies will enhance the functionality and efficiency of gateways, ensuring they meet the growing demands of modern applications:
- 5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will provide enhanced bandwidth and lower latency, enabling smarter and more responsive gateways that can handle a larger number of connected devices without compromising performance.
- IoT Enhancements: The continued advancement of IoT technologies will drive the need for smarter gateways capable of managing complex networks of devices with varied communication protocols.
- Advanced Analytics: The incorporation of sophisticated data analytics tools will allow smart gateways to process and analyze data in real-time, providing actionable insights for users and organizations.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality: AR and VR technologies will create new applications for smart gateways, particularly in sectors such as training, remote assistance, and immersive experiences.
As smart gateways evolve, they will become increasingly critical in shaping the future of connected technologies, driving innovations across multiple industries.
Clarifying Questions
What is a smart gateway?
A smart gateway is a device that facilitates communication and interoperability between various IoT devices and networks.
How do smart gateways improve security?
Smart gateways enhance security by providing centralized control and monitoring of connected devices, enabling better threat detection and response.
Can smart gateways work with different communication protocols?
Yes, smart gateways are designed to support multiple communication protocols, ensuring compatibility across various devices and systems.
What industries benefit from smart gateways?
Industries such as healthcare, transportation, energy, and smart cities benefit significantly from the implementation of smart gateways.
Are smart gateways essential for smart homes?
Yes, smart gateways are essential for smart homes as they enable the integration and management of various smart devices for enhanced convenience and automation.
In today’s tech-savvy environment, optimizing your home network with wi fi google home can significantly enhance your smart devices’ performance. By creating a reliable wireless network, you ensure that devices like smart speakers and lights operate seamlessly, making your daily activities more efficient and enjoyable. Embracing these technologies not only simplifies your life but also elevates your home automation experience to a new level.
For those looking to upgrade their home automation system, the sonoff basic is a fantastic addition. This smart switch allows you to control various appliances remotely, giving you the power to manage your home effortlessly. Whether it’s turning off lights or setting a schedule for your devices, the versatility of the Sonoff Basic can transform your living space into a modern, smart home.